China mim parts
China mim parts
Blog Article

MIM parts, or Metal Injection Molding parts, are precision components created through a process that combines metal powders and binders. These MIM parts excel in producing intricate geometries with minimal machining.
MIM parts achieve tolerances as tight as ±0.1% and densities up to 99% of wrought metals, making them indispensable for industries requiring high precision and efficiency.
Key Takeaways
- MIM parts mix metal powders and binders to form exact shapes. These parts are great for industries like cars and airplanes.
- The MIM process uses less material and works very efficiently. It saves money when making medium to large amounts of parts.
- MIM technology allows creative designs with detailed shapes and accuracy. This lowers the need for extra cutting or shaping later.
What Are MIM Parts?
Definition and Characteristics
MIM parts, or Metal Injection Molding parts, are precision-engineered components created through a process that combines fine metal powders with binders. This method allows manufacturers to produce small, intricate parts with complex geometries that traditional manufacturing methods struggle to achieve. MIM technology offers significant design freedom, enabling the creation of features such as thin walls, undercuts, and sharp edges.
The characteristics of MIM parts make them highly versatile. They can achieve wall thicknesses as thin as 0.5mm with proper design standards. Additionally, they maintain high material density, often reaching 95-99% of wrought metals. This ensures excellent mechanical properties, including strength, corrosion resistance, and thermal stability. MIM parts also support high production volumes, making them cost-effective for large-scale manufacturing.
| Characteristic | Description |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | Optimal thickness is up to 6mm; ultra-thin walls below 0.5mm are possible with high design standards. |
| Yield | MIM allows for high production volumes economically, but small batches increase costs. |
| Raw Materials | Capable of processing various materials including alloys and ceramics, though some are more economical to produce via other methods. |
Key Features and Benefits
MIM parts offer several advantages that set them apart from other manufacturing methods. They provide unparalleled design flexibility, enabling the production of complex 3D geometries and intricate features. This reduces the need for additional machining or assembly, saving time and costs. The process also ensures high dimensional precision, with tolerances as tight as ±0.1%.
The benefits of MIM parts extend to material properties. They achieve densities comparable to wrought metals, ensuring durability and strength. Their corrosion resistance and thermal stability make them suitable for demanding applications, such as automotive, aerospace, and medical industries. Furthermore, MIM technology minimizes material waste, contributing to sustainability efforts.
- Key Benefits of MIM Parts:
- High precision and tight tolerances.
- Broad material compatibility, including stainless steel and titanium alloys.
- Cost-effective for mass production.
- Environmentally friendly due to reduced waste.
MIM parts have revolutionized manufacturing by combining precision, efficiency, and sustainability. Their ability to meet the demands of modern industries underscores their importance in today’s technological landscape.
How Are MIM Parts Made?

Overview of the MIM Process
The Metal Injection Molding (MIM) process combines the precision of injection molding with the strength of metal materials. It is a multi-step manufacturing technique designed to produce complex, high-strength components with exceptional accuracy. This process is particularly advantageous for creating intricate geometries that are difficult to achieve through traditional methods like machining or casting.
MIM offers significant benefits over other manufacturing techniques. It provides greater design freedom, allowing for the production of parts with thin walls, undercuts, and fine details. The process also ensures high material utilization, reducing waste compared to subtractive methods. Additionally, MIM achieves material properties comparable to wrought metals, making it suitable for demanding applications in industries such as aerospace, automotive, and medical devices.
| Stage | Description |
|---|---|
| Mixing | Combining fine metallic powder with binders to create a uniform feedstock |
| Injection molding | Heating and injecting the feedstock into a mold to create the green part |
| Debinding | Removing the binder through solvent or thermal methods |
| Sintering | Heating the debinded part to densify the powder and create a solid metal part |
Step-by-Step Manufacturing Process
The MIM process involves four key stages: mixing, injection molding, debinding, and sintering. Each step plays a critical role in transforming raw materials into finished components.
- Mixing: Fine metallic powders are blended with binders to form a homogeneous feedstock. This mixture ensures uniformity in the final product.
- Injection Molding: The feedstock is heated and injected into a mold, creating a "green part" that retains the desired shape but lacks strength.
- Debinding: The binder is removed from the green part using solvent or thermal methods, resulting in a porous structure known as the "brown part."
- Sintering: The brown part undergoes high-temperature treatment in a controlled atmosphere. This step fuses the metal particles, producing a dense, high-strength component.
The precision and efficiency of these steps make MIM Parts a preferred choice for industries requiring complex, high-performance components.
Materials Used in MIM Parts
Common Materials
Metal Injection Molding (MIM) parts rely on a wide range of materials to meet the diverse needs of industries. Stainless steel dominates the market, accounting for approximately 51.6% of usage in 2024. Its popularity stems from its excellent corrosion resistance, strength, and versatility. Other commonly used materials include aluminum, titanium, and tool steels, each offering unique advantages for specific applications.
- Stainless Steel: Available in austenitic, ferritic, and martensitic grades, it is ideal for applications requiring corrosion resistance and durability.
- Titanium Alloys: Grades such as Ti-6Al-4V provide high strength, lightweight properties, and biocompatibility, making them suitable for medical and aerospace sectors.
- Tool Steels: Known for their hardness and wear resistance, these materials are often used in industrial applications.
- Non-Ferrous Metals: Aluminum and copper alloys are preferred for lightweight and conductive components.
- Superalloys: These materials excel in high-temperature environments, often used in aerospace and energy industries.
Material Properties and Suitability
The properties of materials used in MIM parts directly influence their performance and suitability for various applications. For instance, 316L stainless steel offers proven biocompatibility, making it a top choice for medical devices. Titanium alloys, such as Grade 5 (Ti-6Al-4V), combine high strength with excellent corrosion resistance, ideal for implants and aerospace components.
| Property | Specification/Value |
|---|---|
| Wall Thickness | 0.8mm to 5mm |
| Tolerances | ±0.1% of dimensions |
| Surface Finish | Under 1 μm Ra |
| Minimum Draft Angle | 1-2° |
| Minimum Hole Diameter | 0.5mm |
| Ideal Part Size | 0.5 grams to 500 grams |
These materials enable MIM parts to achieve exceptional precision, durability, and performance, making them indispensable in industries like automotive, aerospace, and medical technology.
Applications of MIM Parts

Industries Utilizing MIM Parts
MIM parts play a critical role across a wide range of industries due to their precision, durability, and cost-effectiveness. These industries rely on MIM technology to produce components that meet stringent performance and quality standards.
- Automotive: MIM parts are widely used in engine components, fuel systems, and transmission systems. Their ability to deliver high strength and tight tolerances makes them ideal for these applications.
- Aerospace: The aerospace sector benefits from MIM parts in landing gear systems, flight control systems, and turbine engines. These components must withstand extreme conditions while maintaining lightweight properties.
- Medical and Dental: MIM technology produces surgical instruments, orthodontic brackets, and implants with exceptional biocompatibility and precision.
- Electronics: High-precision MIM parts are essential for consumer electronics, including connectors, microgears, and heat sinks.
- Pharmaceutical: Devices such as inhalers and drug delivery systems utilize MIM parts for their reliability and intricate designs.
| Industry | Application Areas | Annual Volume |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Fuel injection components, gears | Over 300 million units |
| Aerospace | Engine components, landing gear systems | N/A |
| Electronics | Consumer electronics, medical devices | 50 million units |
| Medical and Dental | Precision parts for surgical and dental applications | Over 20 million units |
Examples of Products
The versatility of MIM parts is evident in the variety of products they help create. These products span multiple industries and demonstrate the adaptability of MIM technology.
| Industry | Example Applications |
|---|---|
| Automotive | Gears, sprockets, rocker arms, connecting rods |
| Aerospace | Turbine blades, impellers, nozzles, valves |
| Medical | Orthodontic brackets, surgical instruments, implants |
| Electronics | Connectors, microgears, screens, printer nozzles |
| Firearms | Triggers, hammers, safeties, ejectors |
| Watches | Gears, pinions, watch hands |
MIM parts have become indispensable in these industries, offering solutions for complex designs and high-performance requirements. Their ability to meet diverse application needs underscores their importance in modern manufacturing.
Advantages of MIM Parts
Cost-Effectiveness
MIM Parts offer significant cost advantages, particularly for medium to high production volumes. The process minimizes material waste, achieving up to 98% material conversion efficiency. This efficiency reduces raw material costs and enhances sustainability. Additionally, MIM consolidates complex, multi-component designs into single parts, eliminating the need for secondary operations and assembly.
Although initial tooling costs for MIM may be higher, the long-term savings are substantial. The reduced material waste and near-net-shape production lower overall manufacturing expenses.
For industries like medical devices, where precision and reliability are critical, MIM provides a cost-effective solution without compromising quality. Manufacturers benefit from lower per-unit costs as production volumes increase, making MIM an attractive option for large-scale operations.
Precision and Complexity
The MIM process excels in producing intricate geometries and high-precision components. It achieves dimensional accuracy within ±0.3%, meeting stringent industry standards. This capability allows manufacturers to create parts with complex shapes that traditional methods cannot replicate.
- MIM supports the production of thin walls, undercuts, and fine details.
- Dimensional precision ensures consistent repeatability, crucial for applications requiring tight tolerances.
The ability to combine precision with complexity makes MIM ideal for industries such as aerospace, automotive, and electronics. These sectors demand components with exceptional mechanical properties and intricate designs.
Scalability for Mass Production
MIM Parts are well-suited for mass production, offering scalability from thousands to millions of units. The process accommodates high-volume manufacturing efficiently, with costs per unit decreasing as production scales.
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| High-Volume Production | MIM is ideal for producing large quantities of complex, lightweight parts. |
| Cost Efficiency | Initial tooling costs are offset by lower costs per unit at higher volumes. |
| Design Flexibility | MIM accommodates complex geometries that traditional methods may not handle. |
The scalability of MIM ensures that manufacturers can meet the demands of large-scale operations without sacrificing quality or precision. This makes it a preferred choice for industries requiring high-performance components at competitive costs.
MIM Parts vs. Other Manufacturing Methods
Comparison with CNC Machining
CNC machining and MIM parts manufacturing serve different purposes, but their comparison highlights the unique advantages of MIM technology. CNC machining excels in producing large, high-precision components, but it struggles with intricate geometries and high production volumes. MIM parts, on the other hand, are ideal for small, complex designs and mass production.
- Precision and Complexity: MIM enables the creation of intricate shapes with tight tolerances, reducing the need for secondary machining.
- Cost-Effectiveness: For medium to high production volumes, MIM offers significant cost savings compared to CNC machining.
- Material Wastage: CNC machining generates more waste due to its subtractive nature, while MIM minimizes material loss.
| Aspect | MIM | CNC Machining |
|---|---|---|
| Cost | More cost-effective for medium to high production volumes | Effective at low volumes |
| Precision | Produces complex geometries with tighter tolerances | Best for accuracy on larger parts |
| Material Wastage | Less material wastage | More material wastage |
| Production Volume | Ideal for mass production | Suitable for low volume production |
MIM parts reduce the need for secondary operations, making them a more efficient choice for industries requiring intricate designs and high output.
Comparison with Casting
Casting methods, such as investment casting, share similarities with MIM in producing metal components. However, MIM parts offer distinct advantages in terms of precision, energy efficiency, and sustainability. Casting often requires higher heat energy and results in more variability due to pressure gradients during mold filling.
- Net Shape Production: MIM produces near-net shape components, reducing post-processing needs.
- Energy Efficiency: MIM requires less heat energy compared to casting, making it more sustainable.
- Material Recovery: Sprues and runners in MIM can be easily recovered and reused, unlike in casting.
| Metric | MIM Parts | Casting Methods |
|---|---|---|
| UTS MPa (ksi) | 860 (125) | 900 (130) |
| YS MPa (ksi) | 758 (115) | 830 (120) |
| Elongation % | 8% | 10% |
| Reduction of Area | 14% | 15% |
| Better Ductility | Yes | No |
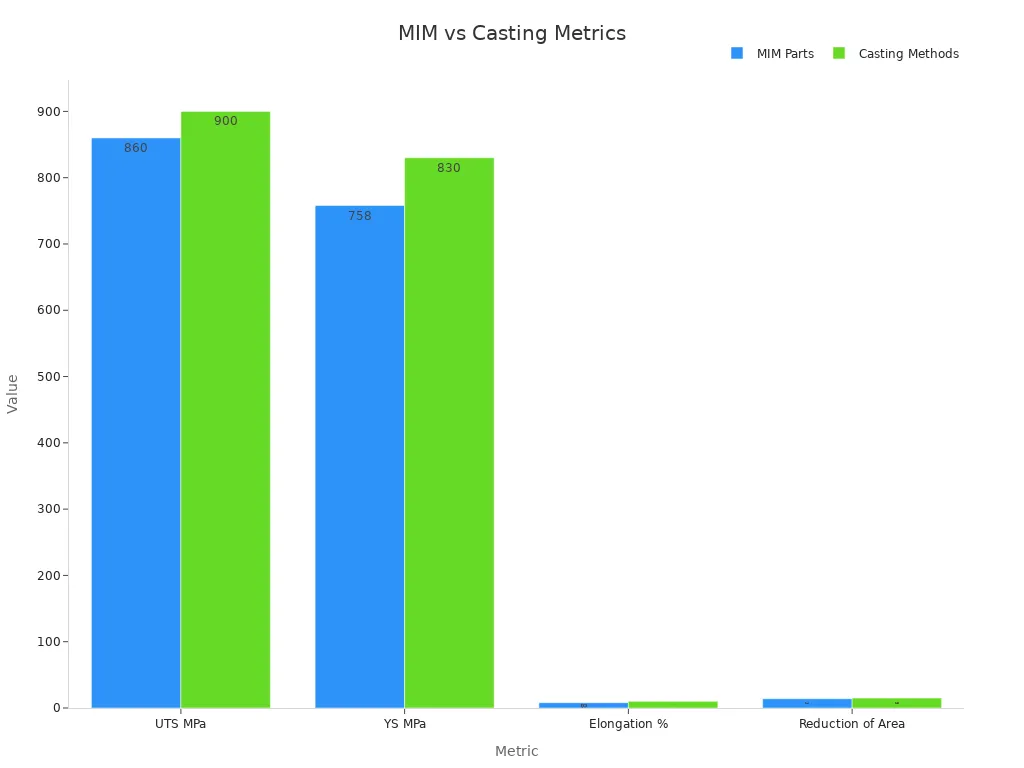
MIM ensures consistent pressure during mold filling, leading to uniformity in parts and lower scrap rates. This consistency makes MIM parts a preferred choice for industries requiring high-quality, repeatable results.
Challenges and Limitations
Potential Drawbacks
While Metal Injection Molding (MIM) offers numerous advantages, it also presents certain challenges that manufacturers must address. One significant drawback is the high initial tooling cost, which makes MIM less suitable for low-volume production. Companies with limited budgets may find these upfront expenses prohibitive. Additionally, MIM struggles with size and weight limitations, as the process is not ideal for components exceeding 500 grams. Mold size and handling constraints further restrict the production of larger parts.
The process also imposes constraints on material selection. While MIM supports a variety of metals, it offers fewer options compared to traditional methods like casting or machining. Achieving very tight tolerances below ±0.5% can also be challenging, particularly for intricate designs. Furthermore, maintaining consistent part sizes across large production runs can prove difficult, potentially impacting quality control.
| Challenge/Limitations | Description |
|---|---|
| Tooling Costs | High initial costs make MIM less viable for low-volume production. |
| Size and Weight Limitations | Difficulties in producing large or heavy components due to mold size constraints. |
| Material Selection Constraints | Limited material options compared to traditional manufacturing methods. |
| Part Size Consistency | Challenges in maintaining consistent part sizes across large production runs. |
| Expensive for Small Production | Cost-effective for large volumes but expensive for small production needs. |
Considerations for Specific Use Cases
MIM technology is best suited for applications requiring high precision and complex geometries in medium to large production volumes. However, manufacturers must carefully evaluate its suitability for specific use cases. For instance, industries requiring parts with extremely tight tolerances or unique materials may need to explore alternative methods. The process also restricts certain geometries due to the debinding and sintering stages, which can limit design flexibility.
- Key Considerations:
- MIM is not ideal for parts exceeding 500 grams or requiring extremely tight tolerances.
- Companies with small production demands may find the process cost-prohibitive.
- Applications involving unique or exotic materials may face compatibility issues.
By understanding these limitations, manufacturers can make informed decisions about whether MIM aligns with their production goals and requirements.
MIM parts have transformed modern manufacturing by combining precision, efficiency, and sustainability. The process enables the creation of intricate components with exceptional material properties, making it ideal for industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical technology. Compared to traditional methods, MIM offers superior design freedom, higher productivity, and cost-effectiveness for medium to large production volumes.
| Advantage | Comparison to Other Processes |
|---|---|
| Design freedom | More flexibility than machining or metal casting |
| Precision | Much higher than sand casting or die casting |
| Material properties | Approaches wrought metals unlike powder metallurgy |
| Productivity | Higher volumes than CNC machining |
| Cost-effectiveness | Lower costs than CNC machining or investment casting for medium+ volumes |
| Sustainability | Less waste than subtractive processes like CNC machining |
The versatility and scalability of MIM parts ensure their continued importance in industries requiring high-precision, cost-effective solutions.
FAQ
What industries benefit the most from MIM parts?
Industries like automotive, aerospace, medical, and electronics benefit significantly. MIM parts provide precision, durability, and cost-efficiency, making them ideal for high-performance applications.
Can MIM parts replace CNC machining for all applications?
No, MIM parts excel in small, intricate designs and mass production. CNC machining remains better for large components or low-volume, high-precision requirements.
Are MIM parts environmentally friendly?
Yes, MIM parts reduce material waste through near-net-shape production. The process also recycles unused materials, contributing to sustainability efforts in manufacturing. Report this page